Agaricus sylvicola (Vittad.) Peck - Wood Mushroom
Phylum: Basidiomycota - Class: Agaricomycetes - Order: Agaricales - Family: Agaricaceae
Distribution - Taxonomic History - Etymology - Identification - Culinary Notes - Reference Sources
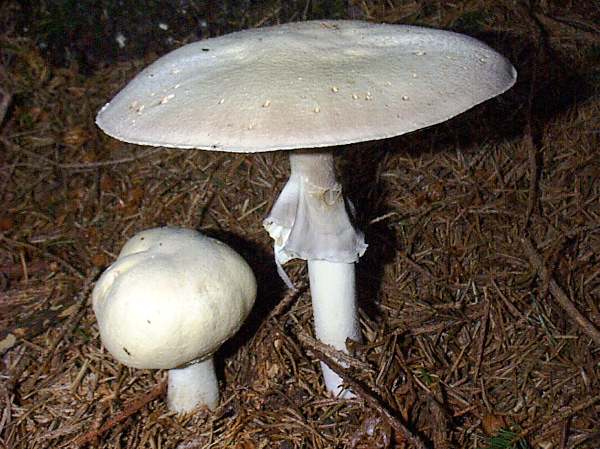

With a noticeable aniseed smell and a smooth cap that slowly colours ochre when bruised, Agaricus sylvicola is quite easily distinguished from the other large mushrooms in the family Agaricaceae. An alternative spelling Agaricus silvicola equally common; this 'orthographic form' is preferred by some authorities. Agaricus sylvicola is the spelling used on Index Fungorum. At the time of writing the majority of online resources including the British Mycological Society use the form 'silvicola'.
Distribution
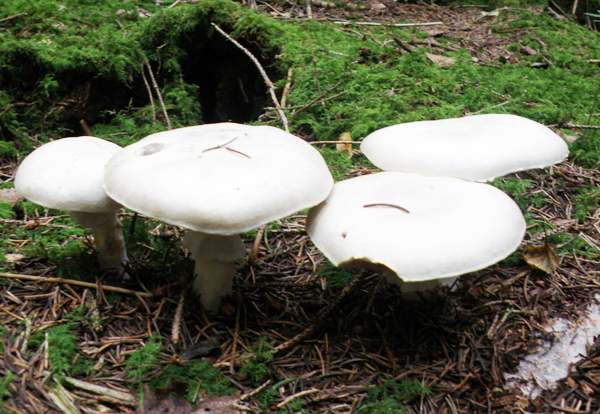
Frequent throughout Britain and Ireland, usually in small, scattered groups but occasionally solitary, Agaricus sylvicola is widely distributed throughout Europe and occurs also in North America. After the Clouded Funnel, Clitocybe nebularis, the Wood Mushroom is probably the most commonly encountered of the large pale forest mushrooms found in Britain and Ireland.

Taxonomic history
First described scientifically in 1832 by Italian obstetrician and (amateur, as all were in those days, and nearly all are today) mycologist Carlo Vittadini (1800 - 1865), this woodland mushroom was considered simply a variety of the Field Mushroom Agaricus campestris and it was given the name Agaricus campestris var. sylvicola. In 1873 an American botanist-mycologist, Charles Horton Peck (1833 - 1917) raised the status of this mushroom to full species level, naming it Agaricus sylvicola.
Synonyms of Agaricus sylvicola include Pratella flavescens Gillet, Psalliota sylvicola (Vittad.) Richon & Roze, and Agaricus essettei Bon. Some authorities treat Agaricus essettei (syn. Agaricus abruptibulbus) as synonymous with Agaricus sylvicola;others treat this chunky mushroom, with its more bulbous stem and on average slightly larger spores, as a distinctly separate species.
Etymology
The specific epithet sylvicola means 'inhabiting woods'.
Identification guide
 |
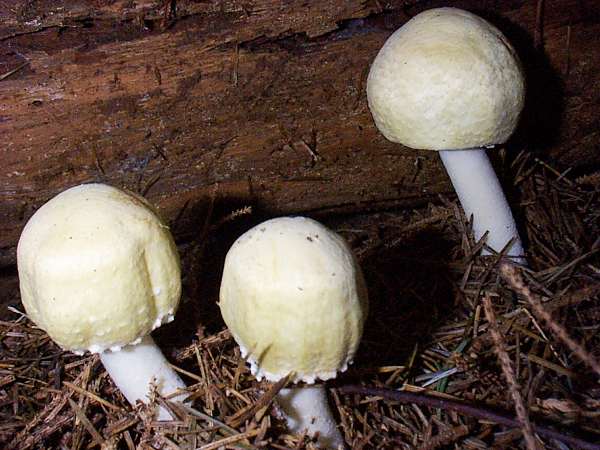
CapThe large white caps of this edible mushroom are initially spherical and then convex before flattening completely at maturity. Pure white at first, the caps tend to yellow with age. Cap diameter when fully developed ranges from 6 to 14cm. |
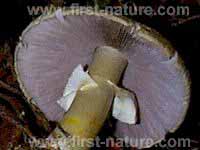 |
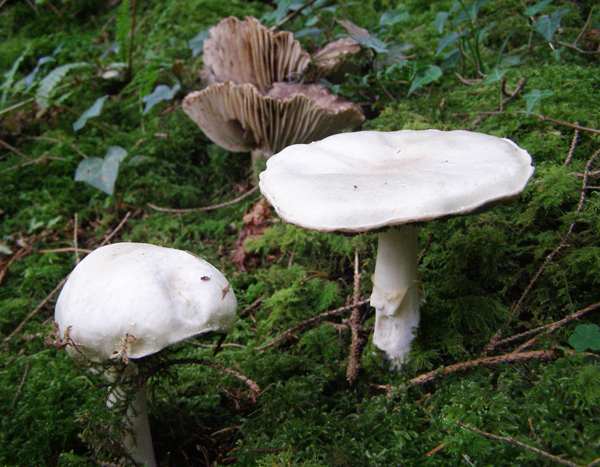
GillsWhite at first, the free gills of the Wood Mushroom turn greyish-pink and then chocolate brown as the spores mature. Stem5 to 8cm tall and 1 to 1.5cm in diameter with a small bulb at the base, the stem of Agaricus sylvicola is white at first and turns yellow-grey as the fruitbody matures. |
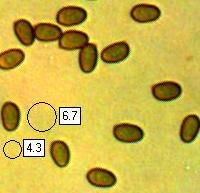 |
SporesEllipsoidal to ovoid, smooth, 5-6.5 x 3.5-4.5µm. Spore printChocolate brown. |
Odour/taste |
Taste not distinctive; odour of aniseed. |
Habitat & Ecological role |
Agaricus sylvicola is saprobic and occurs in all kinds of woodland, usually in trooping groups. |
Season |
August to November in Britain and Ireland; through to February in southern Europe. |
Similar species |
Agaricus arvensis, the Horse Mushroom, is similar in appearance and also has an aniseed smell; it appears in grassland, often growing in rings. Apart from the very different habitat, it would be possible to mistake Wood Mushrooms for Horse Mushrooms, because they look and smell quite similar; however, the stem base of Agaricus sylvicola is relatively longer and slimmer, and it has a noticeably bulbous base. Agaricus xanthodermus quickly stains chrome yellow, both at the edge of the cap and especially when the base of the stipe is cut; it smells of ink or iodine rather than of aniseed. |
Culinary Notes

Although occasional adverse reactions to this mushroom have been reported in North America, I have found no reports of people becoming seriously ill as a result of eating this species, which authorities on edible fungi list as a good edible mushroom. Accurate identification is, of course, essential, and the usual precautions are advisable when trying this or any other mushroom for the first time: start with a small portion to make sure that your body is not intolerant of this partcular species. If you contemplate eating any white-capped woodland mushrooms, make sure that you are able to recognise the two most deadly amanitas that could be picked by mistake: Amanita phalloides, the Deathcap, and Amanita virosa, the Destroying Angel. Amanita ovoidea, the Bearded Amanita, which is extremely rare in Britain, is also a white-capped mushroom but is reported to be safe to eat.
Reference Sources

Fascinated by Fungi, 2nd Edition, Pat O'Reilly 2016, reprinted by Coch-y-bonddu Books in 2022.
BMS List of English Names for Fungi
The genus Agaricus in Britain, 3rd Edition, self-published, Geoffrey Kibby 2011
Funga Nordica: 2nd edition 2012. Edited by Knudsen, H. & Vesterholt, J. ISBN 9788798396130
Dictionary of the Fungi; Paul M. Kirk, Paul F. Cannon, David W. Minter and J. A. Stalpers; CABI, 2008
Taxonomic history and synonym information on these pages is drawn from many sources but in particular from the British Mycological Society's GB Checklist of Fungi.
Fascinated by Fungi. Back by popular demand, Pat O'Reilly's best-selling 450-page hardback book is available now. The latest second edition was republished with a sparkling new cover design in September 2022 by Coch-y-Bonddu Books. Full details and copies are available from the publisher's online bookshop...

