Entoloma prunuloides (Fr.) Quél. - Mealy Pinkgill
Phylum: Basidiomycota - Class: Agaricomycetes - Order: Agaricales - Family: Entolomataceae
Distribution - Taxonomic History - Etymology - Identification - Culinary Notes - Reference Sources
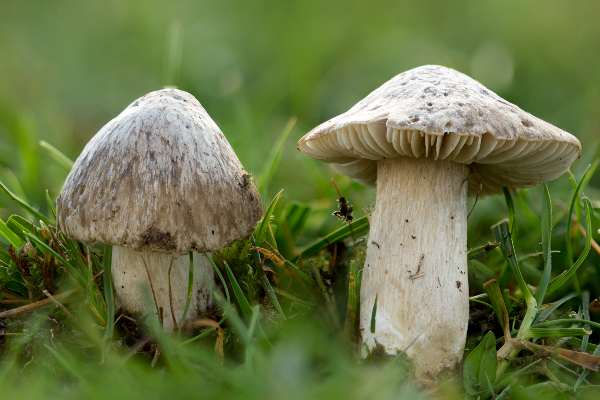

The Mealy Pinkgill Entoloma prunuloides fully deserves its common name, as both the odour and the taste of this grassland mushroom are farinaceous (like wet flour, or meal). In this, however, it is not unique among fungi; for example, St George's Mushroom Calocybe gambosa is also a 'mealy mushroom'..
We are grateful to David Kelly for the pictures shown on this page, the accuracy of which have been independently verified by microscopic examination of samples of gill and cap tissue.
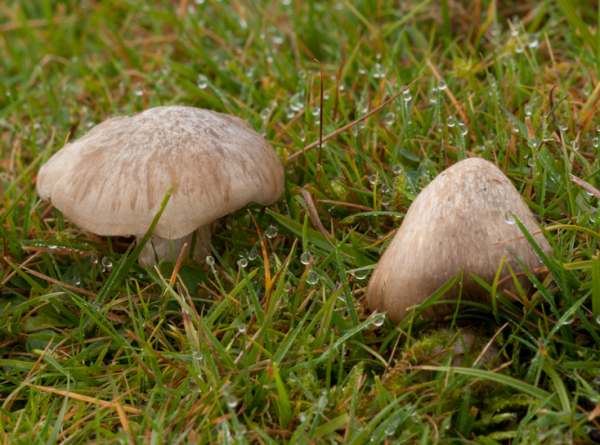

Distribution
The Mealy Pinkgill is an uncommon find in Britain and Ireland, although it is widely distributed; this pinkgill occurs also throughout most mainland Europe, where it rarely more than an occasional find.
Taxonomic history
When in 1821 Elias Magnus Fries described this species in his Systema Mycologicum he gave it the scientific (binomial) name Agaricus prunuloides. (Most gilled mushrooms were, in those early days of fungal taxonomy, initially placed in a gigantic Agaricus genus most of whose occupants have since been redistributed across many new genera.) It was the French Mycologist Lucien Quélet who, in 1872, transferred this species to its present genus, whereupon its scientific name became Entoloma prunuloides.
Synonyms of Entoloma prunuloides include Agaricus prunuloides Fr., Rhodophyllus prunuloides (Fr.) Quél., Entoloma inocybiforme Bon, and Entoloma inopiliforme Bon.
Etymology
The generic name Entoloma comes from ancient Greek words entos, meaning inner, and lóma, meaning a fringe or a hem. It is a reference to the inrolled margins of many of the mushrooms in this genus.
The specific epithet prunuloides means 'similar to prunulus', which in turn is nothing to do with prunes but simply means pruinose - frosted as if covered in a fine white powder.
Identification guide
 |
Cap2 to 7cm across; initially convex becoming plane with an umbo; not hygrophanous; colour varying from white through cream to ochre-brown; surface smooth or inately radially fibrillose but not striate. |
 |
GillsFairly distant, adnate to emarginate; whitish at first, maturing pink. Stem3 to 12cm long and 0.5 to 2.2cm diameter, smooth, cylindrical; white, bruising yellowish red; no stem ring. |
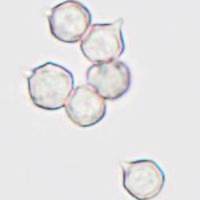 |
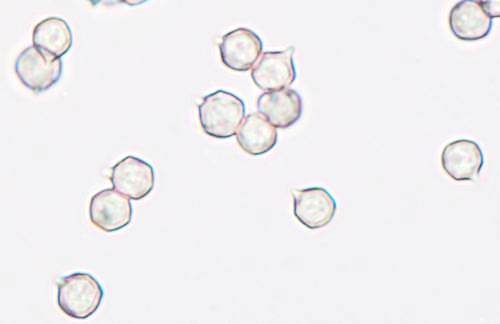
SporesIsodiametrical, thin-walled; 6.5-8 x 6.5-8μm.
Spore printBrownish pink. |
Odour/taste |
Mealy (farinaceous) odour and taste. |
Habitat & Ecological role |
Saprobic in unimproved sheep-grazed grassland. |
Season |
Fruiting from late summer to late autumn. |
Similar species |
Entoloma griseocyaneum has a scaly cap and much larger spores. |
Culinary Notes
Reported in some field guides to be inedible and in others as poisonous, Entoloma prunuloides is definitely not one for the pot. (Some Entoloma species - for example Entoloma sinuatum - are known to be deadly poisonous.).
Reference Sources
Fascinated by Fungi, 2nd Edition, Pat O'Reilly 2016, reprinted by Coch-y-bonddu Books in 2022.
Knudsen H., Vesterholt J. (eds) Funga Nordica: agaricoid, boletoid and cyphelloid genera - Nordsvamp, 2008
Dictionary of the Fungi; Paul M. Kirk, Paul F. Cannon, David W. Minter and J. A. Stalpers; CABI, 2008
Taxonomic history and synonym information on these pages is drawn from many sources but in particular from the British Mycological Society's GB Checklist of Fungi.
Acknowledgements
This page includes pictures kindly contributed by David Kelly.
Fascinated by Fungi. Back by popular demand, Pat O'Reilly's best-selling 450-page hardback book is available now. The latest second edition was republished with a sparkling new cover design in September 2022 by Coch-y-Bonddu Books. Full details and copies are available from the publisher's online bookshop...